[转]一千个不用 Null 的理由
港真,Null 貌似在哪里都是个头疼的问题,比如 Java 里让人头疼的 NullPointerException,为了避免猝不及防的空指针异常,千百年来程序猿们不得不在代码里小心翼翼的各种 if 判断,麻烦而又臃肿,为此 java8 引入了 Optional 来避免这一问题。
下面咱们要聊的是 MySQL 里的 null,在大量的 MySQL 优化文章和书籍里都提到了字段尽可能用NOT NULL,而不是NULL,除非特殊情况。但却都只给结论不说明原因,犹如鸡汤不给勺子一样,让不少初学者对这个结论半信半疑或者云里雾里。本文今天就详细的剖析下使用 Null 的原因,并给出一些不用 Null 的理由。
1. 1、NULL 为什么这么多人用?
- NULL是创建数据表时默认的,初级或不知情的或怕麻烦的程序员不会注意这点。
- 很多人员都以为not null 需要更多空间,其实这不是重点。
- 重点是很多程序员觉得NULL在开发中不用去判断插入数据,写sql语句的时候更方便快捷。
2. 2、是不是以讹传讹?
MySQL 官网文档:
NULL columns require additional space in the rowto record whether their values are NULL. For MyISAM tables, each NULL columntakes one bit extra, rounded up to the nearest byte.
Mysql难以优化引用可空列查询,它会使索引、索引统计和值更加复杂。可空列需要更多的存储空间,还需要mysql内部进行特殊处理。可空列被索引后,每条记录都需要一个额外的字节,还能导致MYisam 中固定大小的索引变成可变大小的索引。
—— 出自《高性能mysql第二版》
照此分析,还真不是以讹传讹,这是有理论依据和出处的。
3. 3、给我一个不用 Null 的理由?
- (1)所有使用NULL值的情况,都可以通过一个有意义的值的表示,这样有利于代码的可读性和可维护性,并能从约束上增强业务数据的规范性。
- (2)NULL值到非NULL的更新无法做到原地更新,更容易发生索引分裂,从而影响性能。
注意:但把NULL列改为NOT NULL带来的性能提升很小,除非确定它带来了问题,否则不要把它当成优先的优化措施,最重要的是使用的列的类型的适当性。
- (3)NULL值在timestamp类型下容易出问题,特别是没有启用参数explicit_defaults_for_timestamp
- (4)NOT IN、!= 等负向条件查询在有 NULL 值的情况下返回永远为空结果,查询容易出错
- (5)Null 列需要更多的存储空间:需要一个额外字节作为判断是否为 NULL 的标志位
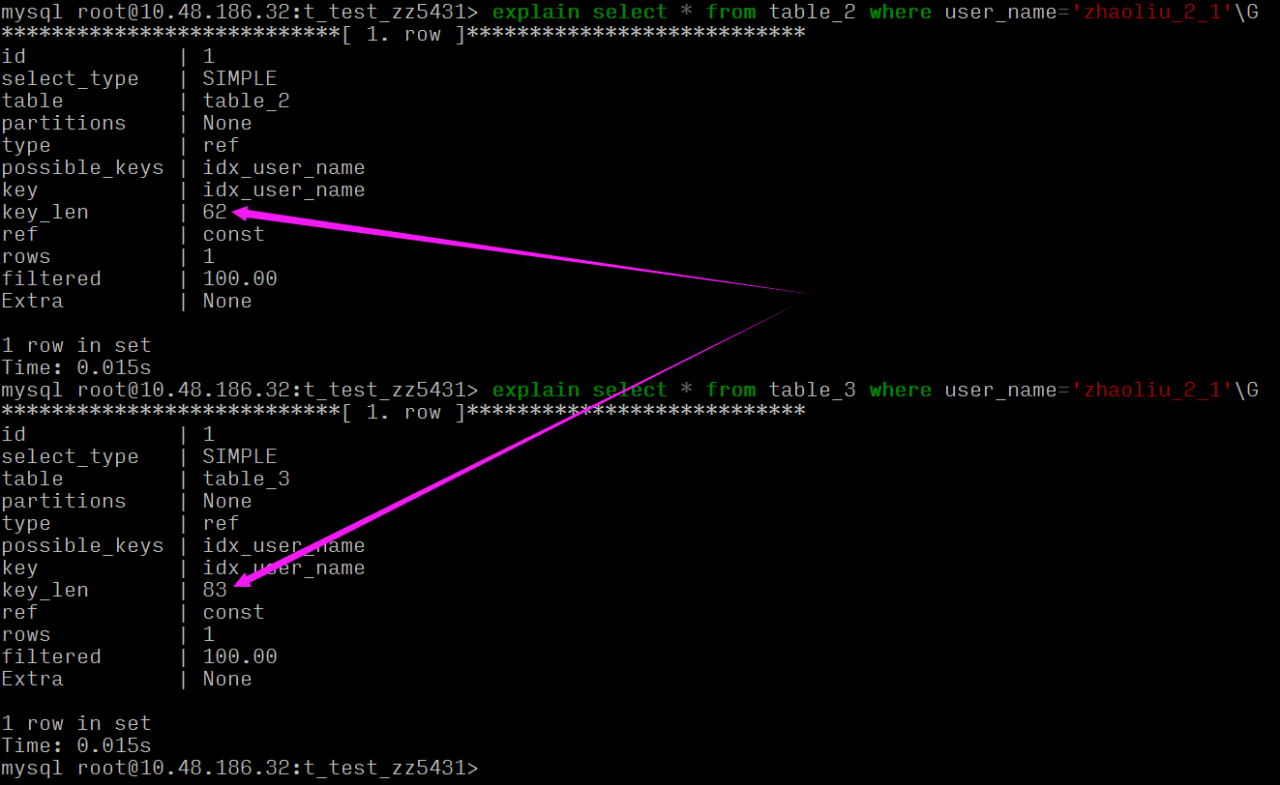
可以看到同样的 varchar(20) 长度,table_2 要比 table_3 索引长度大,这是因为:
两张表的字符集不一样,且字段一个为 NULL 一个非 NULL。
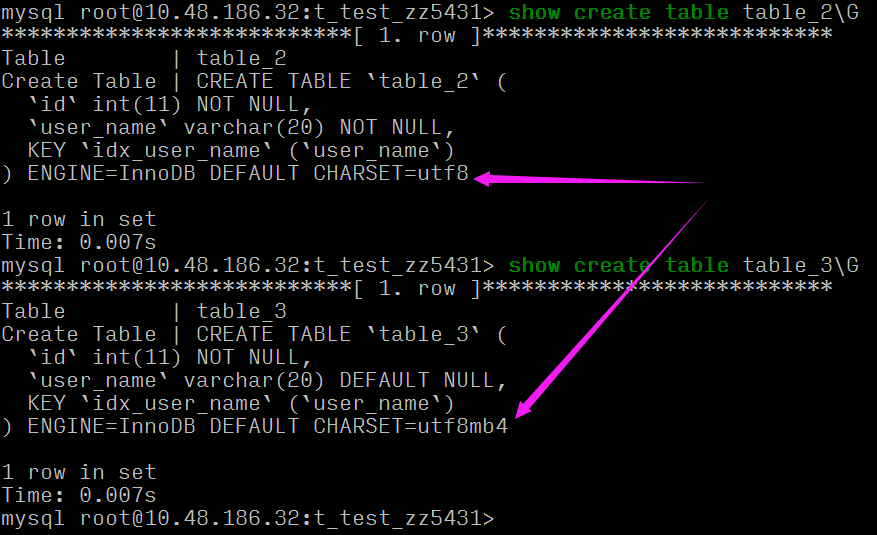
key_len 的计算规则和三个因素有关:数据类型、字符编码、是否为 NULL
key_len 62 == 20*3(utf8 3字节) + 2 (存储 varchar 变长字符长度 2字节,定长字段无需额外的字节)
key_len 83 == 20*4(utf8mb4 4字节) + 1 (是否为 Null 的标识) + 2 (存储 varchar 变长字符长度 2字节,定长字段无需额外的字节)
所以说索引字段最好不要为NULL,因为NULL会使索引、索引统计和值更加复杂,并且需要额外一个字节的存储空间。基于以上这些理由和原因,我想咱们不用 Null 的理由应该是够了
[source]一千个不用 Null 的理由

![[转]SQL效率之where子句中的子查询和函数](http://www.mobabel.net/wp-content/themes/hueman/assets/front/img/thumb-medium-empty.png)
![[汇总]AI经验](http://www.mobabel.net/wp-content/themes/hueman/assets/front/img/thumb-small-empty.png)